- do(x) notation
represents an idealized experiment in which variables
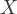 are deliberately set to given values; in the causal diagram, this would correspond to removing all edges entering
are deliberately set to given values; in the causal diagram, this would correspond to removing all edges entering 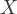 , disconnecting influences of the parents of
, disconnecting influences of the parents of 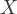 and setting
and setting 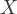 at a value
at a value 
- Excess proportion
a proportion of cases that would not have occurred had the population not been exposed, relative to cases when the entire population was exposed (i.e. counterfactual risk when exposed is compared with counterfactual risk when unexposed)
- Exchangeability
independence of the counterfactual outcome and the actual treatment
- Health services research
a study of the use, organization and outcomes of health services
- Identifiability of causal effects
the causal effect of intervention is identifiable if all backdoor paths between intervention and outcome variables can be blocked in the causal diagram; stratifying on the sufficient set removes all confounding bias in estimates of the causal effect of
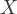 on
on 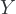
- Indirect effect
the expected change in outcome in response to changing mediating variable to the level it would have attained had exposure changed by one unit, while holding exposure at initial level
- Instrumental variable
a variable relative to the total effect of exposure on outcome if there is a set of measurements, unaffected by the exposure, such the instrument is conditionally independent of the outcome given the set and the instrument is not independent of the exposure conditional on the set