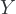- Conditional probability
the quotient of the joint probability of two events in the same space and the marginal probability of one of the events
- Confounding
association between two variables due to a third variable
- Consistency assumption
for a given individual, the observed outcome equals the potential outcome, as a function of intervention, when the intervention is set to the observed level
- Counterfactual reasoning
comparing potential outcomes of alternative interventions with observed outcomes in a thought experiment
- d-separation
variables
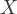 and
and 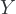 are said to be
are said to be  -separated, if all paths from
-separated, if all paths from 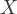 to
to 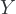 are blocked. A path may be blocked by a set of variables
are blocked. A path may be blocked by a set of variables 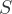 , if the path contains at least one arrow-emitting variable that is in
, if the path contains at least one arrow-emitting variable that is in 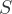 or if the path contains at least one collider that is not in S and has no descendent in
or if the path contains at least one collider that is not in S and has no descendent in 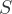 . A collider is defined as a variable on a path such that the path enters and leaves via arrow heads.
. A collider is defined as a variable on a path such that the path enters and leaves via arrow heads. 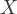 and
and 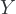 are, therefore,
are, therefore,  -separated conditional on
-separated conditional on 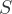 , if
, if 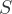 blocks all paths between
blocks all paths between 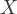 and
and 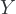 . X and Y are marginally independent when S contains the null set
. X and Y are marginally independent when S contains the null set - Direct effect
the expected change in outcome in response to changing exposure while holding all other variables fixed
- Directed acyclic graph (DAG)
a graph in which nodes represent variables and arrows represent influence between the variables they connect without loops; an arrow drawn from variable
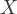 to variable
to variable 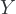 represents a dependency of
represents a dependency of 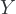 on
on 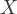 , and no dependency of
, and no dependency of 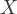 on
on